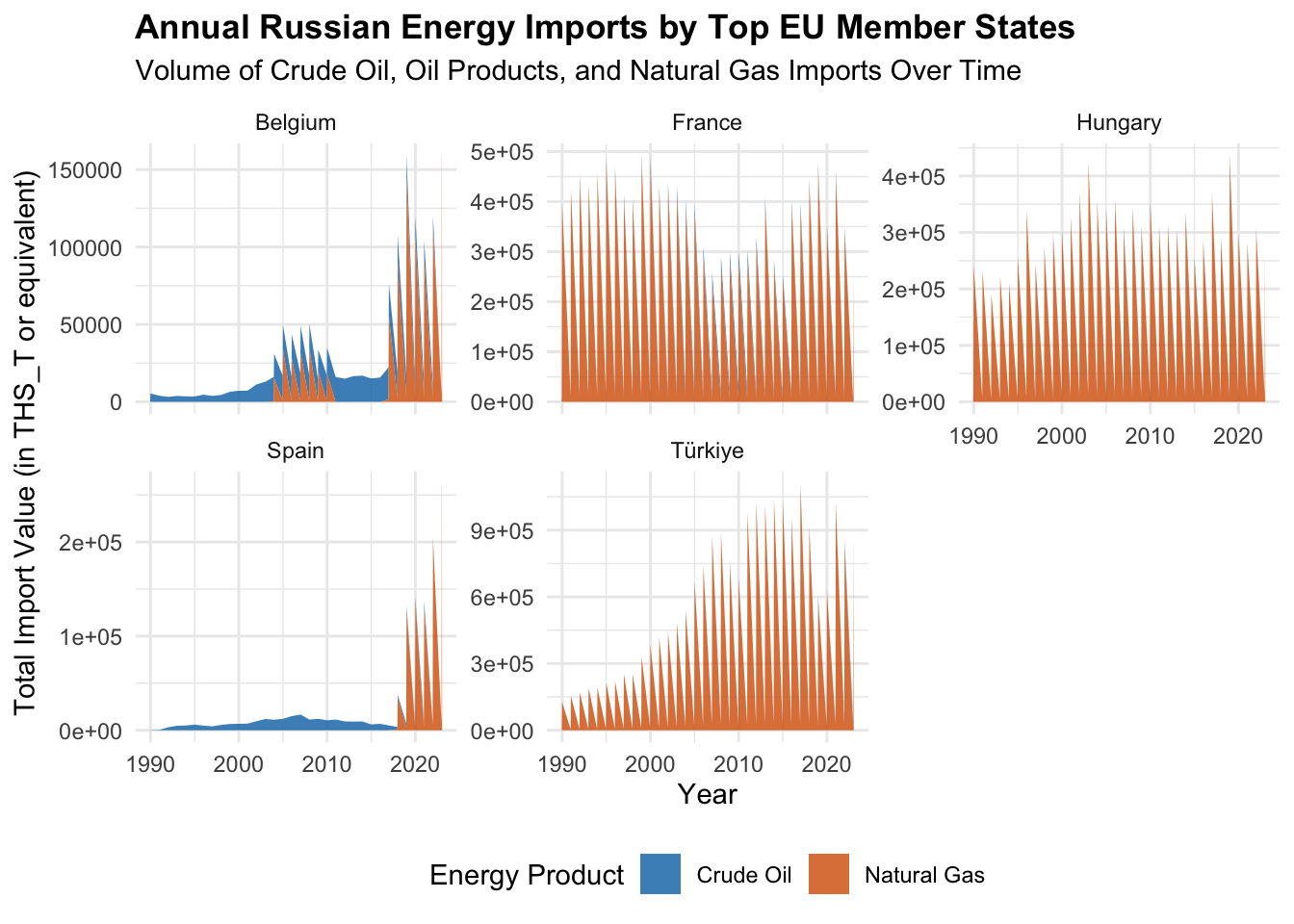
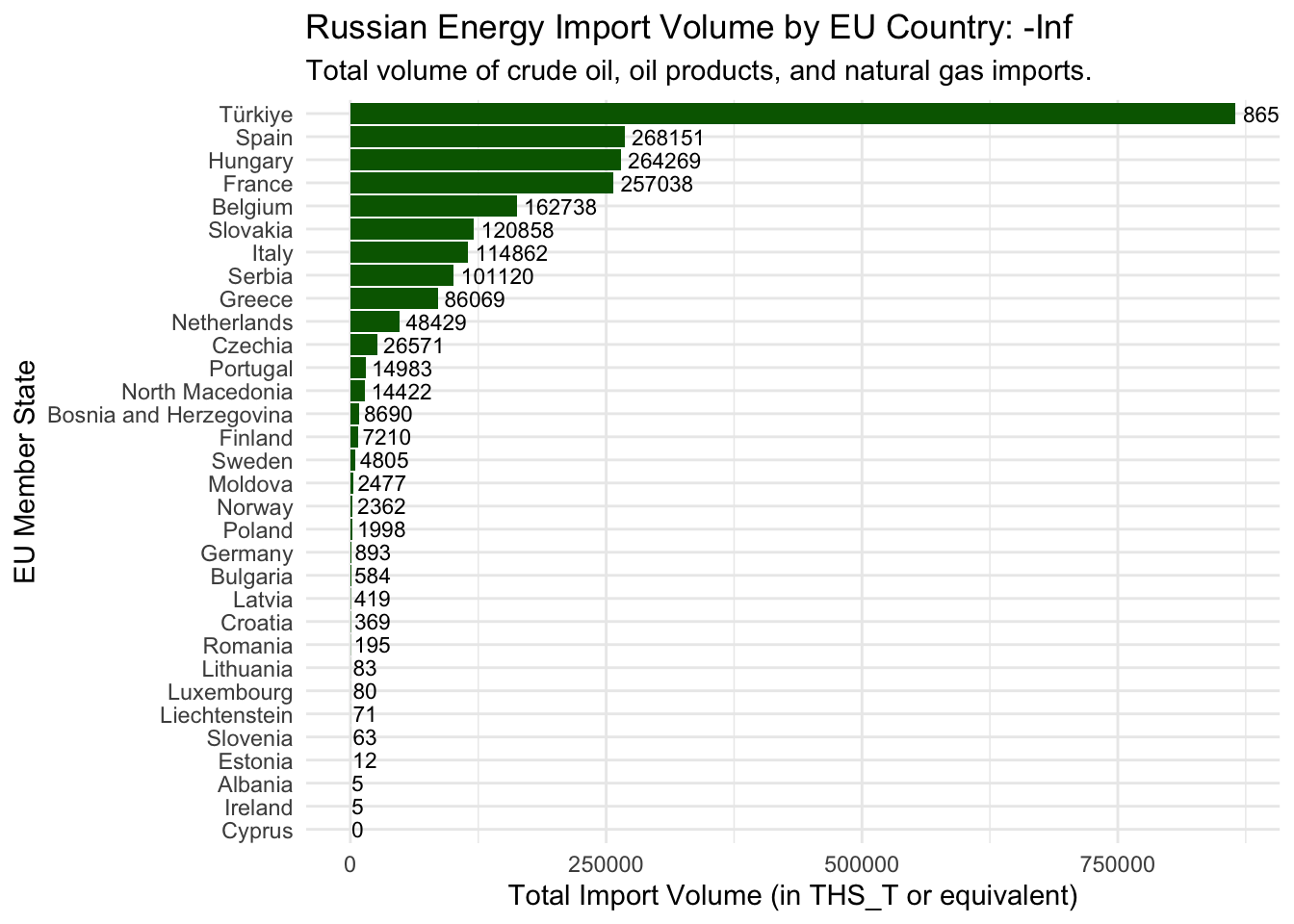
How’s that done?
# Install the eurostat package if you haven't already
# install.packages("eurostat")
library(eurostat)
library(dplyr)
Attaching package: 'dplyr'The following objects are masked from 'package:stats':
filter, lagThe following objects are masked from 'package:base':
intersect, setdiff, setequal, unionHow’s that done?
library(tidyr)
# --- 1. Natural Gas Imports from Russia (nrg_ti_gas) ---
# Dataset code for Imports of natural gas by partner country: nrg_ti_gas
# siec code for Natural gas: G3000
# partner code for Russia: RU
# Geopolitical entity (reporting) (geo) for all EU member states: 'all' will get all reporting countries.
cat("Downloading Natural Gas imports from Russia...\n")Downloading Natural Gas imports from Russia...How’s that done?
# Filters for the get_eurostat() function:
# id: The Eurostat dataset code
# filters: A named list specifying the values for dimensions (e.g., partner, siec)
# time_format: Use 'date' for better time handling
# type: 'code' ensures you get the raw codes, which are easier to filter and label later
gas_data_raw <- get_eurostat(
id = "nrg_ti_gas",
filters = list(
partner = "RU", # Partner country: Russia
siec = "G3000" # Energy product: Natural gas
),
time_format = "date",
type = "code"
)Table nrg_ti_gas cached at /var/folders/f2/q8xv3f0x6mb9ks58ht339qmsr_x3qc/T//Rtmp2X4JyT/eurostat/c84be0b07215aa5a10caa65eb9774806.rdsHow’s that done?
# Process the gas data
gas_data_clean <- gas_data_raw %>%
# Select and rename key columns
select(
geo_code = geo,
time = time,
unit_code = unit,
value = values
) %>%
# Remove rows with missing values (e.g., confidential data)
filter(!is.na(value)) %>%
# Add a product column
mutate(product = "Natural Gas")
# --- 2. Oil and Petroleum Product Imports from Russia (nrg_ti_oil) ---
# Dataset code for Imports of oil and petroleum products by partner country: nrg_ti_oil
# partner code for Russia: RU
# The 'siec' dimension in this dataset typically includes 'O4000' (Crude oil) and 'O4400_TOT' (Oil products)
# To get the total, we might omit siec or use a combined code if available.
# Let's start by getting all oil/petroleum products (O-codes) from Russia.
cat("Downloading Oil and Petroleum Product imports from Russia...\n")Downloading Oil and Petroleum Product imports from Russia...How’s that done?
# Download all oil and petroleum products from Russia
oil_data_raw <- get_eurostat(
id = "nrg_ti_oil",
filters = list(
partner = "RU", # Partner country: Russia
siec = c("O4000", "O4400_TOT") # Crude oil (O4000) and Oil products (O4400_TOT)
),
time_format = "date",
type = "code"
)Table nrg_ti_oil cached at /var/folders/f2/q8xv3f0x6mb9ks58ht339qmsr_x3qc/T//Rtmp2X4JyT/eurostat/57f466e228a4f9af673c946852e506f0.rdsHow’s that done?
# Process the oil data
oil_data_clean <- oil_data_raw %>%
select(
geo_code = geo,
time = time,
unit_code = unit,
value = values,
siec_code = siec
) %>%
filter(!is.na(value)) %>%
# Map SIE-C codes to product names for clarity
mutate(
product = case_when(
siec_code == "O4000" ~ "Crude Oil",
siec_code == "O4400_TOT" ~ "Oil Products",
TRUE ~ "Other Oil/Petroleum"
)
) %>%
select(-siec_code) # Remove the raw SIE-C code column
# --- 3. Combine and Label Data ---
# Combine the gas and oil data frames
all_energy_imports <- bind_rows(gas_data_clean, oil_data_clean)
# Get the full country names for the 'geo' codes
geo_labels <- get_eurostat_dic("geo", lang = "en") %>%
rename(geo_code = code, country_name = label)Error in `rename()`:
! Can't rename columns that don't exist.
✖ Column `code` doesn't exist.How’s that done?
# Join the labels to the main dataset and finalize
final_data_russia_imports <- all_energy_imports %>%
left_join(geo_labels, by = "geo_code") %>%
# Reorder columns for readability
select(
country_name,
country_code = geo_code,
time,
product,
unit_code,
value
) %>%
# Filter to keep only EU Member States (or other relevant reporting entities if 'all' was used)
# Eurostat geo codes like 'EU27_2020' are aggregates, you might want to filter them out
# or keep them based on your exact needs. We'll filter for country-level data.
filter(
!grepl("^EU|^EA|^EFTA|^WLD|^XK", country_code) # Exclude large aggregates
) %>%
# Spread the data slightly if preferred (optional, for summary viewing)
arrange(country_name, product, time)Error: object 'geo_labels' not foundHow’s that done?
# Display the first few rows of the final data
cat("\n--- First 10 rows of the Combined Data ---\n")
--- First 10 rows of the Combined Data ---How’s that done?
print(head(final_data_russia_imports, 10))Error: object 'final_data_russia_imports' not foundHow’s that done?
# Display the data structure
cat("\n--- Data Structure ---\n")
--- Data Structure ---How’s that done?
print(glimpse(final_data_russia_imports))Error: object 'final_data_russia_imports' not foundHow’s that done?
# You can save the data to a CSV file
# write.csv(final_data_russia_imports, "russia_energy_imports_eurostat.csv", row.names = FALSE)